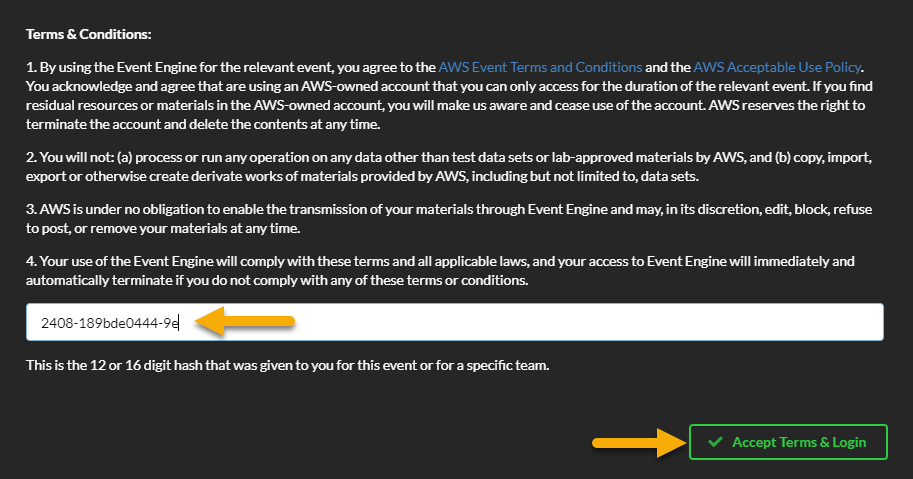
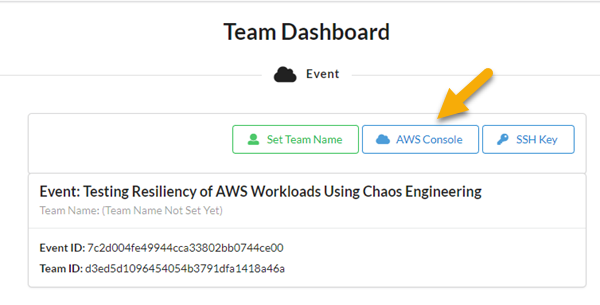
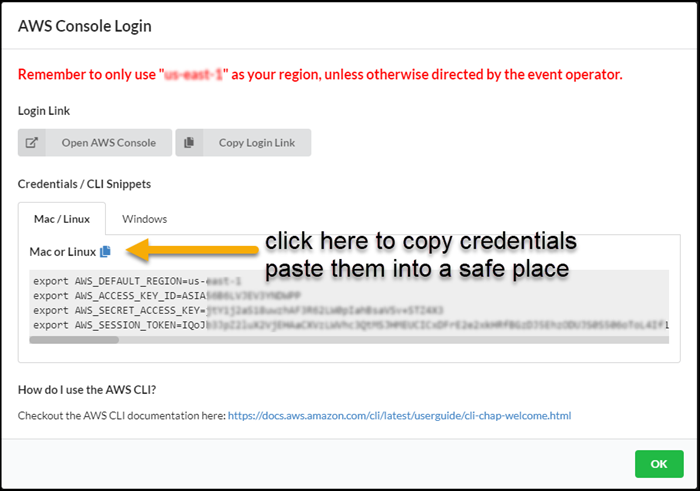
Setup AWS credentials and configuration
- You will supply configuration and credentials used by the AWS CLI and AWS SDK to access your AWS account.
Choose an option
Select the appropriate option for configuration of your AWS credentials:
- Option 1 - Using AWS instructor supplied accounts with Linux-style environment variables
- Option 2 - Using AWS CLI
- Option 3 - Creating configuration files manually
- Option 4 - Using PowerShell commands for Windows
Option 1 For instructor supplied AWS accounts
If BOTH of the following are true then you may use Option 1
- If you are attending an in-person workshop and were provided with an AWS account by the instructor then you should use this option
- You are running the workshop on a system where environment variables are set using the
exportcommand, such as Bash on Amazon Linux
Otherwise you should choose Option 2 or Option 3
You should have already copied the credentials for your account. If not then:
The copied credentials are already in the form of
exportstatements. Run these from your shell command line. Use your values, not the ones belowexport AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=ASIIAMFAKENOPZLX6J5L export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=w0pE4j5k4FlUrkIIAMFAKEdiLMKLGZlxyct+GpTam export AWS_SESSION_TOKEN=FQoGZXIvYXdzEDwaIIAMFAKEn0LVImWNQHiLuAWKe+KFkLeIvpOHEruWjyCjrEdyjtW8WCbnmJGM1ES20xq1fcaS5TERHDUabZJ60Kk6nc9uHoCDb1QKHi+MerRIcKJTi3OKz0QMVPAGVqVWgvOBBSQ2lylLVjtMMSQF+yLZsP1bvehQ0ke/Bl/X6RJySOHg2TZGyESPL/INqJiZyEHi+MelAnThepVgWUKFPD5mESBVlpy2LVCE3xPpHFqOm0Q79svRSSW2jLj5NkRXL+xhkcvt+g8vNt1ODEwixwMGpFB2sBHryv6EXNeX6c88vxJ8Zyfkmsqi0xmCW1f9jWAPIXNkt/nEYW4J4coyLKP7QU= export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=us-east-2Also run this command as written below
export AWS_DEFAULT_OUTPUT=jsonNote that if you end your bash session, or start a new one, you will need to re-execute the
exportstatements
If you completed Option 1 then STOP HERE and return to the Lab Guide
Option 2 AWS CLI
This option uses the AWS CLI. You should use Option 3 if you do not or cannot install the AWS CLI.
To see if the AWS CLI is installed:
$ aws --version aws-cli/1.16.249 Python/3.6.8...- AWS CLI version 1.1 or higher is fine
- If you instead got
command not foundthen either install the AWS CLI or use Option 3
Run
aws configureand provide the following values:$ aws configure AWS Access Key ID [*************xxxx]: <Your AWS Access Key ID> AWS Secret Access Key [**************xxxx]: <Your AWS Secret Access Key> Default region name: [us-east-2]: us-east-2 Default output format [None]: json
Option 3 Manually creating credential files
If you already did Option 2, then skip this
create a
.awsdirectory under your home directorymkdir ~/.awsChange directory to there
cd ~/.awsUse a text editor (vim, emacs, notepad) to create a text file (no extension) named
credentials. In this file you should have the following text.[default] aws_access_key_id = <Your access key> aws_secret_access_key = <Your secret key>Create a text file (no extension) named
config. In this file you should have the following text:[default] region = us-east-2 output = json
Configure a session token as part of your credentials
If you used Option 2 or Option 3, please follow these steps:
- Determine if you need to configure a session token as part of your credentials
| AWS Account | Do you need a session token? |
|---|---|
| You are attending an in-person workshop and were provided with an AWS account by the instructor | yes |
| You are using your own AWS account, and using credentials from an IAM User (most common case) | no |
| You are using your own AWS account, and using credentials from an IAM Role | yes |
- Do this only if “yes”, you need to configure a session token
Edit the file
~/.aws/credentialsThe
defaultprofile will already be present. Under it add an entry foraws_session_token[default] aws_access_key_id = <Your access key> aws_secret_access_key = <Your secret key> aws_session_token = <your session token>
Clear environment variables
If you used option 2 or option 3 then you have put your credentials into files that will be used by the AWS CLI or AWS SDK. However these will preferentially use credentials and configuration in environment variables. Therefore ensure that the following env variables are not set:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_SESSION_TOKENAWS_DEFAULT_REGIONAWS_DEFAULT_OUTPUTAWS_PROFILE
How to do this varies depending on system. For Linux:
# Use echo $varname to see if it is set
$ echo $AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
ASIATWOQ3L72RPLOP222
# use unset
$ unset AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
# This now returns no value
$ echo $AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
For your convenience:
unset AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
unset AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
unset AWS_SESSION_TOKEN
unset AWS_DEFAULT_REGION
unset AWS_DEFAULT_OUTPUT
unset AWS_PROFILE
Option 4 (PowerShell)
If you do not have the AWS Tools for Powershell, download and install them following the instructions here. https://aws.amazon.com/powershell/.
Start a Windows PowerShell for AWS session. If prompted for AWS Secret Key during initialization, type Control-C to break out of the dialog.
Configure your AWS credentials with the following PowerShell commands. Note that if you are using an instructor supplied AWS account, you must include the optional SessionToken flag and value as shown below in brackets (omit the brackets when running the command):
Set-AWSCredentials -AccessKey <Your access key> -SecretKey <Your secret key> \
[ -SessionToken <your session key> ] -StoreAs <SomeProfileName>
Initialize-AWSDefaults -ProfileName <SomeProfileName> -Region us-east-2
Return to the Lab Guide to continue the lab